- U5a1a
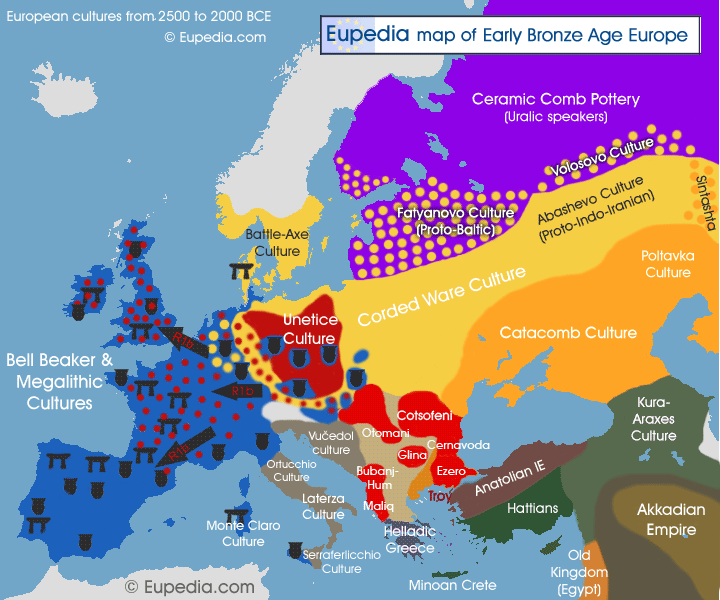
- U5a1a1: found mostly in northern, central and eastern Europe and in Central Asia (Uzbekistan) / found in the Afanasievo and Yamna cultures and in Chalcolithic Germany (Bell Beaker)
- U5a1a1a: found in Poland
- U5a1a1b: found in Sweden
- U5a1a1c: found in Sweden
- U5a1a1d: found in the British Isles and Scandinavia
- U5a1a2: found in England, Scandinavia, Central Europe and Turkey / found in Chalcolithic Germany (Bell Beaker)
HVR1 MATCHES
| Austria | 1 | 1346 | 0.1% | |
| Germany | 1 | 16134 | < 0.1 % | |
| Italy | 2 (my wife) | 5046 | < 0.1 % |
Siculo-Norman Hauteville dynasty
Hauteville-la-Guichard
Sanctuary of the Holy Bed
|
|---|
|
|---|
Parish church dedicated to the cult of the Holy Cross of Christ. Ecclesial complex, seat of the Monastery of S. Stefano, of Norman origin (about 11th to 12th century).
|
South German (Swabian) Hohenstaufen.
Charlemagne’s family is known to have hailed from Swabia. The Welf (Azzolina) family went on to rule in Bavaria and Hanover, and are ancestral to the British Royal Family that has ruled since 1714.
Norman/Germanic Heritage through Sicily, Italy at Santo Stefano di Camastra, Messina, Sicily, Italy. Constantinople – Constantinople was the capital city of the Roman/Byzantine, and also of the brief Latin, and the later Ottoman empires. Thrace is a geographical and historical area in southeast Europe, now split between Bulgaria, Greece and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south and the Black Sea to the east.
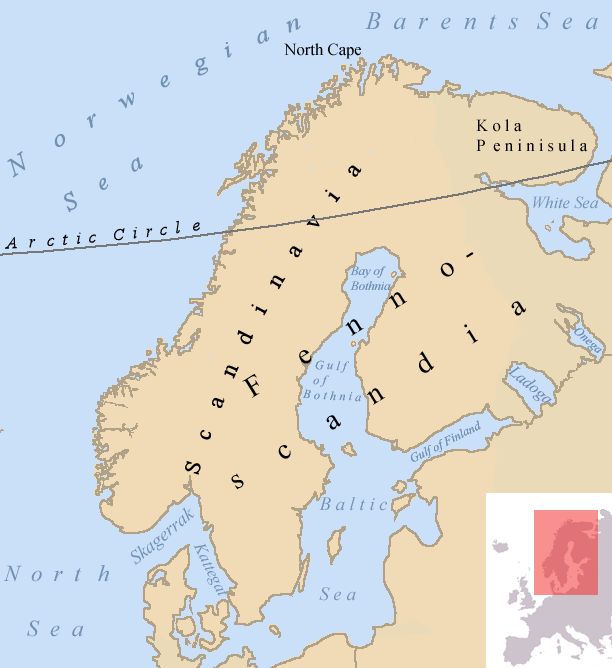
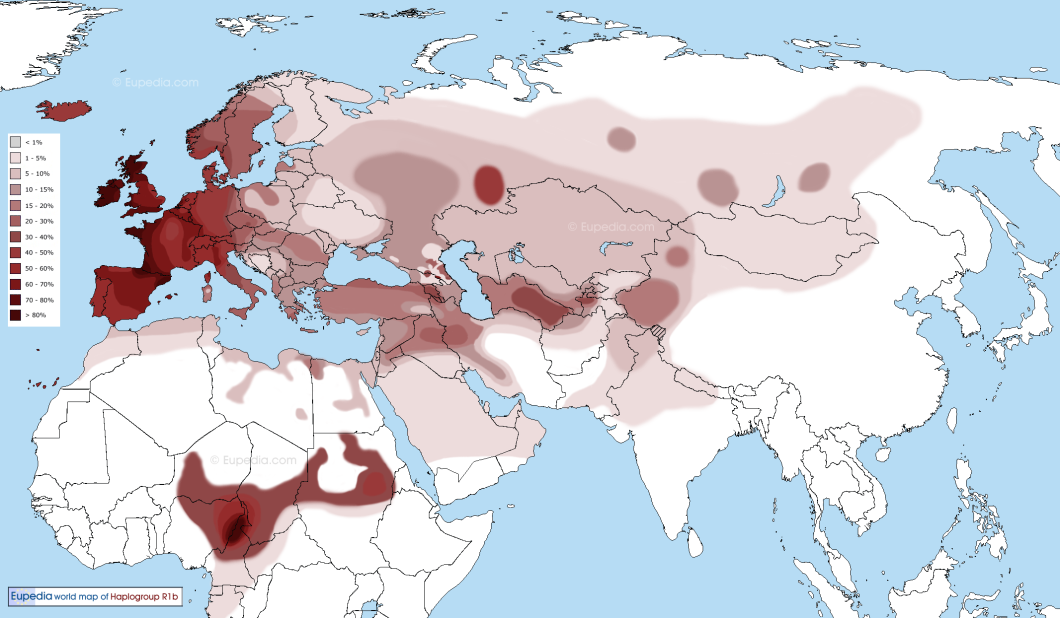
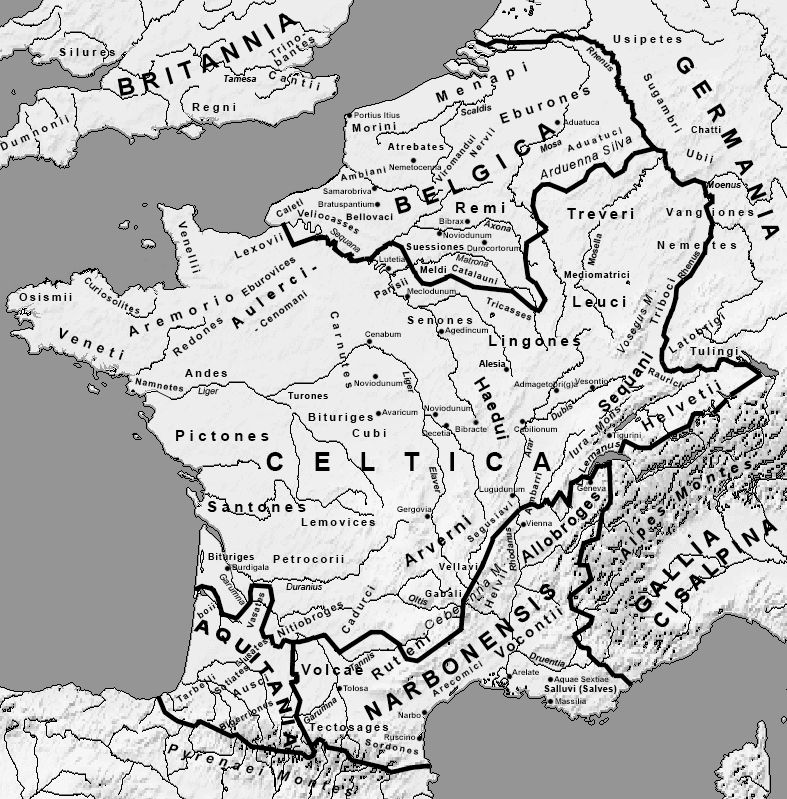
Haplogroup U5 is found throughout Europe with an average frequency ranging from 5% to 12% in most regions. U5a is most common in north-east Europe and U5b in northern Spain. Nearly half of all Sami and one fifth of Finnish maternal lineages belong to U5. Other high frequencies are observed among the Mordovians (16%), the Chuvash (14.5%) and the Tatars (10.5%) in the Volga-Ural region of Russia, the Estonians (13%), the Lithuanians (11.5%) and the Latvians in the Baltic, the Dargins (13.5%), Avars (13%) and the Chechens (10%) in the Northeast Caucasus, the Basques (12%), the Cantabrians (11%) and the Catalans (10%) in northern Spain, the Bretons (10.5%) in France, the Sardinians (10%) in Italy, the Slovaks (11%), the Croatians (10.5%), the Poles (10%), the Czechs (10%), the Ukrainians (10%) and the Slavic Russians (10%). Overall, U5 is generally found in population with high percentages of Y-haplogroups I1, I2, and R1a, three lineages already found in Mesolithic Europeans. The highest percentages are observed in populations associated predominantly with Y-haplogroup N1c1 (the Finns and the Sami), although N1c1 is originally an East Asian lineage that spread over Siberia and Northeast Europe and assimilated indigenous U5 maternal lineages.
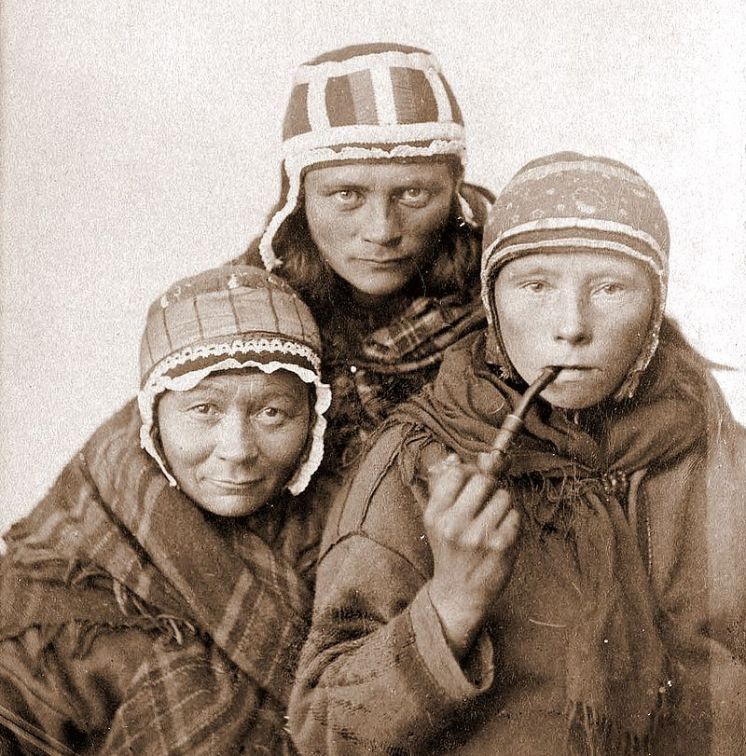
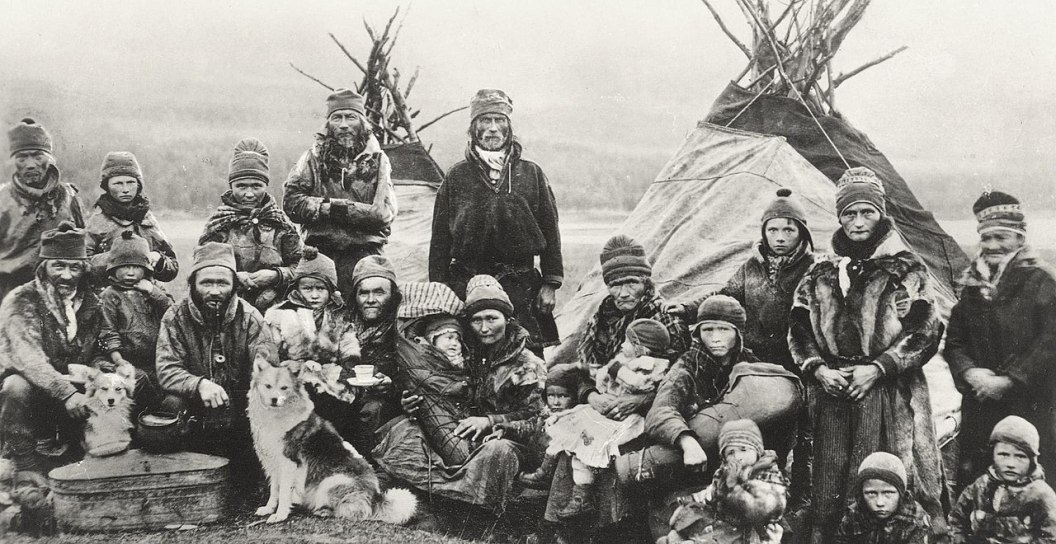
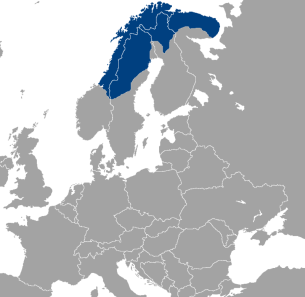
The Sami people (also known as the Sámi or the Saami) are a Finno-Ugric people inhabiting Sápmi, which today encompasses large parts of Norway and Sweden, northern parts of Finland, and the Murmansk Oblast of Russia. The Sami have historically been known in English as the Lapps or the Laplanders, but these terms can be perceived as derogatory. Sami ancestral lands are not well-defined. Their traditional languages are the Sami languages and are classified as a branch of the Uralic language family.
Sápmi, in English commonly known as the now-pejorative term Lapland, is the cultural region traditionally inhabited by the Sami people, traditionally known in English as Lapps. Sápmi is located in Northern Europe and includes the northern parts of Fennoscandia. The region stretches over four countries: Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Russia. On the north it is bounded by the Barents Sea, on the west by the Norwegian Sea and on the east by the White Sea.
Sápmi: 63,831–107,341
Norway: 37,890–60,000
Sweden: 14,600–36,000
Finland: 9,350
Russia: 1,991
Ukraine: 136
https://racitidesigns.wordpress.com/2018/03/18/haplogroup-u5-mtdna-indigenous-nordic-sami-finnish-peoples-fennoscandia/